Banish Bad Breath for Good: Effective Ways to Get Rid of Bad Breath
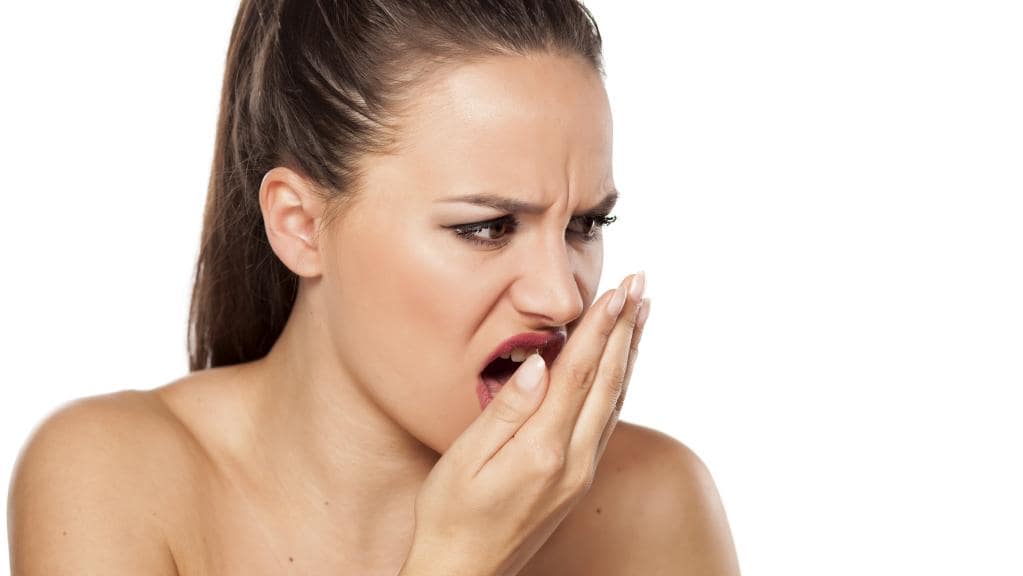

Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a common oral health issue that can be both embarrassing and frustrating. Understanding the root causes of bad breath is essential in effectively addressing and eliminating this condition. Fortunately, with the implementation of proper oral hygiene practices, dietary adjustments, and the use of mouthwash and natural remedies, you can combat bad breath and regain your confidence. In more severe cases, seeking professional guidance from a dentist can provide valuable insights and personalized solutions. Let’s delve into the effective ways to get rid of bad breath and restore fresh breath for good.
Understanding the Causes of Bad Breath
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be embarrassing and affect your confidence. Understanding the root causes of bad breath is crucial in effectively addressing the issue and implementing the right solutions.
Common Causes of Bad Breath:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and the accumulation of food particles, causing an unpleasant odor.
-
Consumption of Certain Foods: Foods like garlic, onions, and spices can contribute to bad breath due to their strong odors.
-
Dry Mouth: Saliva helps cleanse the mouth, so a reduction in saliva flow, often experienced during sleep, can lead to bad breath.
-
Tobacco Products: Smoking or using tobacco-based products can leave chemicals that contribute to bad breath.
-
Underlying Health Issues: Certain medical conditions such as gum disease, diabetes, respiratory tract infections, and acid reflux can also cause bad breath.
By understanding these common causes, you can take proactive steps to address and get rid of bad breath effectively. Establishing good oral hygiene practices, making dietary adjustments, and seeking professional dental care when necessary are essential in combating bad breath at its source.
Effective Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to get rid of bad breath. Here are some effective oral hygiene practices that can help you achieve fresh breath and a healthy mouth:
-
Brushing:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a toothbrush with soft bristles to gently clean all surfaces of your teeth and your tongue.
-
Flossing:
- Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth and along the gumline.
- Make it a habit to floss at least once a day to prevent the buildup of odor-causing bacteria.
-
Tongue Scraper:
- Use a tongue scraper to gently clean your tongue. Odor-causing bacteria can accumulate on the tongue’s surface, contributing to bad breath.
-
Hydration:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist and reduce odor-causing bacteria.
By integrating these oral hygiene practices into your daily routine, you can effectively get rid of bad breath and maintain optimal oral health. Regular dental check-ups are also essential to address any underlying dental issues contributing to persistent bad breath.
The Role of Diet in Bad Breath
What you eat can have a significant impact on the freshness of your breath. Making mindful choices about your diet can help you get rid of bad breath and keep it at bay. Here’s how your diet can affect your breath:
-
Avoid Strong-Smelling Foods: Certain foods like garlic, onions, and spices can contribute to bad breath. When these foods are digested, their strong-smelling compounds enter the bloodstream and are carried to the lungs, affecting your breath.
-
Drink Plenty of Water: A dry mouth can lead to bad breath, so staying hydrated is crucial. Water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of developing bad breath.
-
Consume Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Crisp, fresh fruits and vegetables like apples, carrots, and celery act as natural teeth cleaners. Their crunchy texture helps remove plaque and food particles from your teeth, reducing the chances of bad breath.
-
Choose Sugar-Free Gum and Mints: Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free mints can stimulate saliva production, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria in the mouth.
Being mindful of what you eat and incorporating breath-friendly choices into your diet can go a long way in helping you get rid of bad breath and maintain fresh breath throughout the day.
Using Mouthwash and Natural Remedies
When it comes to dealing with bad breath, using mouthwash and natural remedies can be highly effective. Here are some ways to incorporate these methods into your oral hygiene routine:
-
Alcohol-Free Mouthwash: Opt for an alcohol-free mouthwash as alcohol can dry out the mouth, exacerbating bad breath. Look for mouthwashes that contain antibacterial agents to target the root cause of the odor.
-
Natural Remedies: Incorporate natural remedies such as chewing on parsley, mint, or cloves to freshen your breath. These natural ingredients contain antibacterial properties that can help combat the bacteria causing bad breath.
-
Oil Pulling: Consider oil pulling with coconut oil. Swishing a tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for 15-20 minutes can help reduce the presence of bacteria and improve overall oral hygiene.
-
Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help flush out bacteria and food particles, thus reducing bad breath.
By incorporating these mouthwash and natural remedy practices into your daily routine, you can effectively combat bad breath and improve your overall oral health, giving you the confidence of fresh breath throughout the day. Remember, these methods complement, but do not replace, regular brushing and flossing to "get rid of bad breath".
Consulting a Dentist
When home remedies and oral hygiene practices don’t effectively address bad breath, it’s time to consult a dentist. A dental professional can provide valuable insight and personalized solutions to help get rid of bad breath for good. Here’s why consulting a dentist is crucial:
-
Professional Evaluation: A dentist can conduct a thorough examination to identify any underlying dental issues contributing to bad breath, such as gum disease, decay, or oral infections.
-
Personalized Treatment Plan: After diagnosing the root cause, the dentist can create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs, which may include professional dental cleanings, periodontal treatments, or restorative procedures.
-
Expert Recommendations: Dentists can recommend specialized oral care products, such as antibacterial mouthwashes or tongue scrapers, to target the specific cause of bad breath.
-
Long-Term Prevention: By addressing oral health problems proactively, a dentist can help you prevent future instances of bad breath, promoting overall oral health and hygiene.
Consulting a dentist is a proactive step towards achieving long-term relief from bad breath, ensuring not only fresh breath but also optimal oral health.
Preventing Bad Breath in the Long Term
To ensure that you can get rid of bad breath and prevent it from recurring in the long term, it’s essential to incorporate good oral hygiene habits into your daily routine. Here are some effective strategies to help you maintain fresh breath consistently:
-
Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with your dentist to address any underlying dental issues and to receive professional cleanings.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist and to wash away food particles and bacteria.
-
Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in sugary and acidic foods to promote overall oral health.
-
Quit Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting. Smoking not only causes bad breath but also increases the risk of gum disease and other oral health problems.
-
Proper Brushing and Flossing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove food particles and plaque, which can contribute to bad breath.
By adopting these practices and being consistent with them, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of bad breath and promote a healthier mouth and fresher breath in the long term.